Knee Replacement Surgery
Also known as arthroplasty, is one of the most commonly performed surgeries with excellent outcomes and patient satisfaction if performed by a skilled and experienced Joint Replacement Surgeon
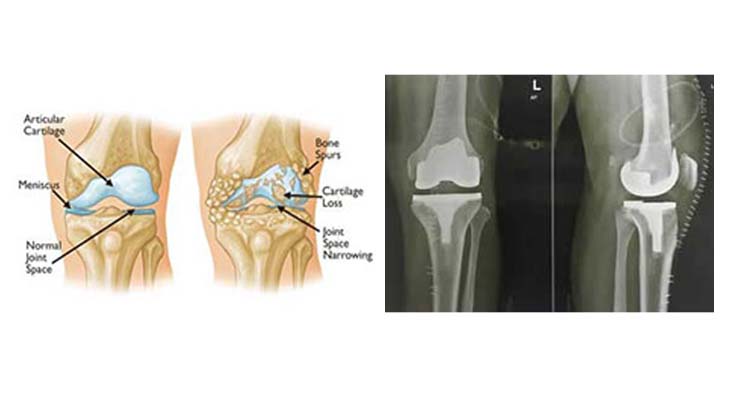
The objective of a Knee Replacement Surgery is to resurface the parts of the knee joint that have been damaged and to relieve knee pain that cannot be controlled by other treatments. There are several causes that can lead to issues in the knee joints.
Arthritis is a degenerative joint disease that is one of the most common ailments that affect your knees, causes the breakdown of joint cartilage and adjacent bone in the knees causing pain and discomfort to the individual. Similarly, in Rheumatoid Arthritis, inflammation of the synovial membrane results in excessive synovial fluid which can lead to pain and stiffness.
Decision of surgery is most likely when
- Severe pain and stiffness make it hard for you to walk, climb stairs, or get out of a chair.
- Continuous knee pain bothers you while resting, possibly keeping you from sleeping well.
- Your knee is often swollen.
- There is a crepitus and tenderness on examination and the patient complains of a crackling sound on bending or flexing the knee.
- Waddling is present while walking
- Your knee is bowed or has other defects.
- Physical therapy and medication haven’t helped.
- Walking is becoming difficult without support
Types of Knee Replacement Procedures
Knee joint replacement is a procedure that involves replacing an injured or affected knee with an artificial joint, or prosthesis that is mostly made of inert metal alloys, ceramic, and polymers. During the surgery, the damaged cartilage and bone are removed from your joint and replaced with a prosthetic component that takes over the shape and movement of a natural joint. The three core areas involved in knee joint replacement are:
- The lower portion of the thigh bone (Femur),
- The upper end of the shinbone (Tibia), and
- Behind the kneecap known as patella
Partial or Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA) Surgery
Subject to the extent of damage in your knee joint, total knee replacement or unicompartmental (partial) knee replacement surgery will be advised to you.
Because a partial knee replacement is done through a smaller incision, patients usually spend less time in the hospital and return to normal activities sooner than total knee replacement patients. The knee is divided into three major compartments:
- Medial compartment (the inside part of the knee)
- Lateral compartment (the outside part)
- Patellofemoral compartment (the front of the knee between the kneecap and thighbone)
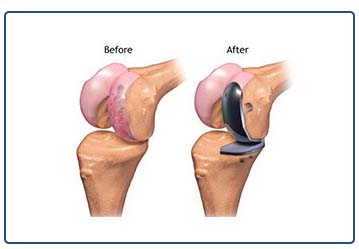
Advanced Osteoarthritis that is limited to a single compartment may be treated with a unicompartmental knee replacement. The medial compartment of the knee joint degeneration is the most common deformity of arthritis. During this procedure, the damaged compartment is replaced with metal and plastic.
Advantages of Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA)
- The healthy cartilage and bone, as well as all of the ligaments, are preserved
- Patients feel lighter and more natural than total knee replacement
- Comes back to all his normal life quite earlier than total knee replacement.
- The incision is smaller, blood loss is also less so shorter recovery period
- Hospital length of stay is also lesser