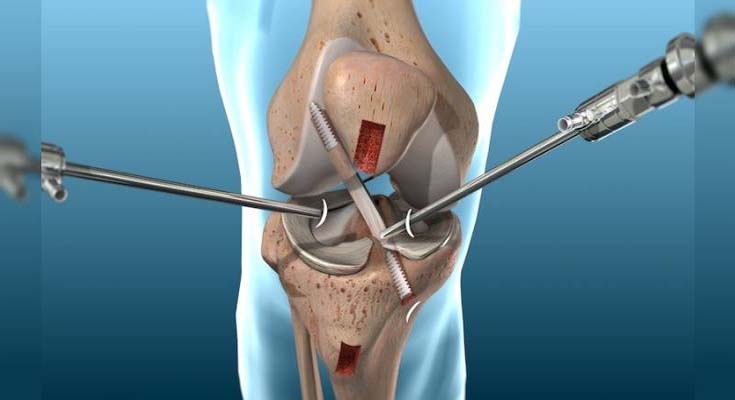
Knee Arthroscopy
Knee Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical procedure performed for joint problems of the knee.
How Knee Arthroscopy is Done:
Knee arthroscopy is performed using a pencil-sized instrument called an Arthroscope. The arthroscope consists of a light system and camera to project images to a computer screen for your surgeon to view the surgical site. Arthroscopy is used to treat disease conditions and injuries involving the bones, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and muscles of the knee joint.
Because the arthroscope and surgical instruments are thin, your surgeon can use very small incisions, rather than the larger incision needed for open surgery. This results in less pain for patients, less joint stiffness, and often shortens the time it takes to recover and return to your favourite activities.
When is Knee Arthroscopy Recommended
Your doctor may recommend knee arthroscopy if you have a painful condition that does not respond to non-surgical treatment. Non-surgical treatment includes rest, physical therapy, and medications or injections that can reduce inflammation.
Knee arthroscopy may help relieve painful symptoms of many problems that damage the cartilage surfaces and other soft tissues surrounding the knee joint.
Common Arthroscopic Procedures for the Knee Include:
- Repair of a torn meniscus
- Reconstruction of a torn ligament
- Removal of inflamed synovial tissue
- Trimming of damaged articular cartilage
- Removal of loose fragments of bone or cartilage
- Treatment of patella or kneecap
- Treatment of knee infection
Preparing for Knee Arthroscopy:
To help plan your procedure, your orthopaedic surgeon may order preoperative tests. These may include blood tests or an electrocardiogram. Be sure to inform your orthopaedic surgeon of any medications or supplements that you take. You may need to stop taking some of these before surgery. The hospital will contact you ahead of time to provide specific details of your procedure. Make sure to follow the instructions on when to arrive and especially on when to stop eating or drinking prior to your procedure.
Before your surgery, an anaesthesiologist will talk with you. Knee arthroscopy can be performed under local, regional, or general anaesthesia:
- Local anaesthesia numbs just your knee
- Regional anaesthesia numbs you below the waist
- General anaesthesia puts you to sleep
Your orthopaedic surgeon and your anaesthesiologist will talk to you about which method is best for you.
Knee Arthroscopy Procedure:
Once you are moved into the operating room, you will be given anaesthesia. To help prevent surgical site infection, the skin on your knee will be cleaned. Your leg will be covered with surgical draping that exposes the prepared incision site.
At this point, a positioning device is sometimes placed on the leg to help stabilise the knee while the arthroscopic procedure takes place.
To begin the procedure, the surgeon will make a few small incisions, in your knee. A sterile solution will be used to fill the knee joint and rinse away any cloudy fluid. This helps your orthopaedic surgeon see the structures inside your knee clearly and in great detail.
Your surgeon’s first task is to properly diagnose your problem. The surgeon will insert the arthroscope and use the image projected on the screen to guide it. If surgical treatment is needed, your surgeon will insert tiny instruments through other small incisions.
Specialised instruments are used for tasks like shaving, cutting, grasping, and meniscal repair. In many cases, special devices are used to anchor stitches into bone.
The length of the surgery will depend upon the findings and the treatment necessary.
Your surgeon may close each incision with a stitch or small band-aids, and then cover your knee with a soft bandage.
Keep your leg elevated as much as possible for the first few days after surgery. Apply ice as recommended by your doctor to relieve swelling and pain.
While recovery from knee arthroscopy is faster than recovery from traditional open knee surgery, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully after you return home.
You should exercise your knee regularly for several weeks after surgery. This will restore motion and strengthen the muscles of your leg and knee.
Many people recover completely after arthroscopy. Your recovery will depend on the type of damage that was present in your knee.
Advantages of Knee Arthroscopy
The advantages of arthroscopy compared to open surgery with a large incision include
- Less pain
- Fewer complications
- Shorter hospital stay
- Faster recovery
Correct rehabilitation for Knee Arthroscopy is very important for recovery. Ranka Orthopedic Hospital offers patients the opportunity to do so at our specialist centre in Pune.